和你一起轻松愉快的刷题
一、前言
- 为了方便阅读,完整笔记分为两篇文章,第(1)篇题目为1-38题,第(2)篇题目为39-75题。
- 所有题目均来自《剑指 Offer(第 2 版)》。
- 截止到编写文章时,所有题解代码均可通过LeetCode在线评测,即AC。
- 笔记中一些题目给出了多种题解和思路,本笔记大多数题解都是较为完美的解法,消耗时间和空间较少。
- 由于作者水平有限,欢迎大家指教,共同交流学习。
- 最后祝大家刷题愉快。
二、开始刷题
剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
哈希表判重
遍历数组元素,加入到哈希表中,当出现重复时,返回该元素。
class Solution {
public:
int findRepeatNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, bool> hash;
for(int num: nums){
if(hash[num])
return num;
hash[num] = true;
}
return -1;
}
};剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
数组元素处理
从右上角开始查找,若当前值大于待搜索值,向左移动一位;若当前值小于待搜索值,向下移动一位。如果最终移动到左下角时仍不等于待搜索值,则说明待搜索值不存在于矩阵中。
class Solution {
public:
bool findNumberIn2DArray(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
if(matrix.empty()){
return false;
}
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
while(i < m && j >= 0){
if(matrix[i][j] == target){
return true;
}else if(matrix[i][j] < target){
++i;
}else{
--j;
}
}
return false;
}
};剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
字符串原地修改
统计空格的个数,修改字符串的长度,双指针倒序遍历修改。
str.resize(int len); // 调整字符串的长度
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
int cnt = 0;
int len = s.size();
for(int i=0; i<s.size(); ++i){
if(s[i] == ' '){
cnt++;
}
}
int new_len = len + cnt*2;
s.resize(new_len);
for(int i=len-1, j=new_len-1; i<j; --i, --j){
if(s[i] == ' '){
s[j] = '0';
s[j - 1] = '2';
s[j - 2] = '%';
j -= 2;
}else{
s[j] = s[i];
}
}
return s;
}
};剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
递归思想打印元素
使用数组保存链表中从前到后的元素,reverse数组或者直接返回一个逆序的数组。
reverse(arr.begin(), arr.end()); // 反转数组中的元素
arr.rbegin() <==> arr.end()
arr.rend() <==> arr.begin()
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
if(!head){
return vector<int>();
}
vector<int> result;
while(head){
result.push_back(head->val);
head = head->next;
}
reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
// return vector<int>(result.rbegin(), result.rend());
}
};剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
前序遍历 + 中序遍历 => 后序遍历
前序遍历的形式总是:
[ 根节点, [左子树的前序遍历结果], [右子树的前序遍历结果] ]
中序遍历的形式总是:
[ [左子树的中序遍历结果], 根节点, [右子树的中序遍历结果] ]利用递归的方法建立二叉树,利用前序遍历和中序遍历的形式特点来确定当前子树的根节点。另外用哈希表预处理中序遍历的结果加速优化,可以更快速查找数字的位置。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
unordered_map<int, int> index;
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int n = preorder.size();
// 构造哈希映射,快速定位根节点在中序遍历的位置
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
index[inorder[i]] = i;
}
return buildTreeHelper(preorder, inorder, 0, n-1, 0, n-1);
}
TreeNode* buildTreeHelper(const vector<int>& preorder, const vector<int>& inorder, int preorder_left, int preorder_right, int inorder_left, int inorder_right) {
// 不存在子树,返回空
if(preorder_left > preorder_right){
return NULL;
}
// 根节点在前序遍历中的位置
int preorder_root = preorder_left;
// 根节点在中序遍历中的位置
int inorder_root = index[preorder[preorder_root]];
// 建立根节点
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorder_root]);
// 左子树的节点数量
int size_left_subtree = inorder_root - inorder_left;
// 递归构造左子树
// 先序遍历:[左边界+1,左边界+左子树节点数目]
// 中序遍历:[左边界,根节点定位-1的元素]
root->left = buildTreeHelper(preorder, inorder, preorder_left+1, preorder_left+size_left_subtree, inorder_left, inorder_root-1);
// 递归构造右子树
// 先序遍历:[左边界+1+左子树节点数目,右边界]
// 中序遍历:[左边界,根节点定位-1]
root->right = buildTreeHelper(preorder, inorder, preorder_left+size_left_subtree+1, preorder_right, inorder_root+1, inorder_right);
return root;
}
};剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
栈实现队列
队列先进先出,栈先进后出,所以还需要另外一个栈来反转数组中的元素,实现先进先出。这个翻转过程既可以在插入时完成,也可以在取值时完成。
class CQueue {
stack<int> in, out;
public:
CQueue() {
}
void appendTail(int value) {
in.push(value);
}
int deleteHead() {
in2out();
if(!out.empty()){
int x = out.top();
out.pop();
return x;
}
return -1;
}
void in2out(){
if(out.empty()){
while(!in.empty()){
int x = in.top();
in.pop();
out.push(x);
}
}
}
};
/**
* Your CQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* CQueue* obj = new CQueue();
* obj->appendTail(value);
* int param_2 = obj->deleteHead();
*/剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列
斐波那契问题
动态规划思想,三个变量保存值。
class Solution {
public:
int fib(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 0;
if(n == 1) return 1;
int ans = 0;
int first = 0, second = 1;
for(int i=2; i<=n; ++i){
ans = (first + second) % 1000000007;
first = second;
second = ans;
}
return ans;
}
};剑指 Offer 10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题
斐波那契问题
青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶或2级台阶,
F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2)。动态规划思想,三个变量保存值。
class Solution {
public:
int numWays(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 1;
if(n == 1) return 1;
int ans = 0;
int first = 1, second = 1;
for(int i=2; i<=n; ++i){
ans = (first + second) % 1000000007;
first = second;
second = ans;
}
return ans;
}
};剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
旋转数组
二分法,即使数组被旋转过,仍然可以利用这个数组的递增性,使用二分查找。
左排序数组任一元素 >= 右排序数组任一元素,旋转点就是右排序数组的第1个元素。
当 nums[mid] > nums[r] 时: mid 一定在 左排序数组 中,即旋转点 x 一定在 [mid + 1, r] 闭区间内,因此执行 l = mid + 1;
当 nums[mid] < nums[r] 时: mid 一定在 右排序数组 中,即旋转点 x 一定在[l, mid] 闭区间内,因此执行 r = mid;
当 nums[mid] = nums[r] 时: 无法判断 mid 在哪个排序数组中,即无法判断旋转点 x 在 [l,mid] 还是 [mid + 1, r] 区间中。解决方案:--r,缩小判断范围,继续二分。
为什么不用 nums[mid]和 nums[l] 作比较?
二分目的是判断 mid 在哪个排序数组中,从而缩小区间。而在 nums[mid] > nums[l] 情况下,无法判断 mid 在哪个排序数组中。本质上是由于 r 初始值肯定在右排序数组中; l 初始值无法确定在哪个排序数组中。
示例,当 l = 0, r = 4, mid = 2 时,有 nums[mid] > nums[l] ,而结果不同。
[1, 2, 3, 4 ,5] 旋转点 x = 0 : mid 在右排序数组;
[3, 4, 5, 1 ,2] 旋转点 x = 3 : mid 在左排序数组。
class Solution {
public:
int minArray(vector<int>& numbers) {
int l = 0, r = numbers.size() - 1;
while(l < r){
int mid = l + (r - l)/2;
if(numbers[mid] == numbers[r]){
// 无法判断
--r;
}else if(numbers[mid] < numbers[r]){
// 向左部分二分
r = mid;
}else{
// 向右部分二分
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return numbers[l];
}
};剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径
矩阵搜索问题
DFS + 回溯 + 剪枝
class Solution {
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
for(int i=0; i<m; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j){
if(dfs(board, word, i, j, 0)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// 方向数组
int dx[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word, int x, int y, int k){
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
if(x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || board[x][y] != word[k]){
return false;
}
if(k == word.size() - 1){
return true;
}
board[x][y] = '.'; // 标记该位置已走过
bool res = false;
for(int i=0; i<4; ++i){
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if(dfs(board, word, nx, ny, k+1)){
return true;
}
}
board[x][y] = word[k]; // 回溯
return false;
}
};剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子
整数拆分
1、数学推导
- 4 : 2*2
- 5 : 2*3
- 6 : 3*3
- 7 : 2*2*3 或 4*3
- 8 : 2*3*3
- 9 : 3*3*3
- 10:2*2*3*3 或 4*3*3
- 11:2*3*3*3
- 12:3*3*3*3
- 13:2*2*3*3*3 或 4*3*3*3
k[0] 到 k[m] 只可能是 2 或者 3,当然也可能有 4,但是 4 = 2*2,也可以不考虑。5 < 2*3,6 < 3*3,比 6 更大的数字我们就更不用考虑了,肯定要继续拆分。
2 的数量肯定小于 3 的数量,因为 2*2*2 < 3*3。
由于题目规定 m > 1,所以 2 只能是 1,3 只能是2,这两个特殊情况直接返回就行了。
2、动态规划
dp[n] = max(dp[n], dp[i] * dp[n-i]);
j <= i/2 是因为 f(5) = f(1)*f(4),f(5) = f(2)*f(3),f(5) = f(3)*f(2),f(5) = f(4)*f(1) ,故遍历一半即可,必须是小于等于。
// 数论
class Solution {
public:
int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n == 2 || n == 3){
return n - 1;
}
int mmax = 1;
while(n > 4){
mmax *= 3;
n -= 3;
}
mmax *= n;
return mmax;
}
};// 动态规划
class Solution {
public:
int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n == 2 || n == 3){
return n - 1;
}
vector<int> dp(n + 1, 0);
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 2;
dp[3] = 3;
// 2、3不能再拆分了,拆了会更小
for(int i=4; i<=n; ++i){
for(int j=1; j<=(i/2); ++j){
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] * dp[i-j]);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II
整数拆分
和 I 相比,II 增大了整数 n 的范围,涉及了 “大数越界情况下的求余问题” 。
本题只能用数学推导,不能用动态规划了,动态规划的取余之后 max 函数就不能用来比大小了,比如取余后 2000000014(0) 会小于 1000000020(13)。
可以将保存结果的变量设置为 long 或 long long 类型,防止溢出,也可以采用快速幂。
class Solution {
public:
int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n == 2 || n == 3){
return n - 1;
}
long mmax = 1;
int mod = 1000000007;
while(n > 4){
mmax *= 3;
mmax %= mod;
n -= 3;
}
mmax *= n;
mmax %= mod;
return (int)mmax;
}
};剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中1的个数
二进制处理
1、bitset 类库
bitset<位数> foo; // 无参构造,默认每一位为0
bitset<位数> foo(二进制数); // 构造函数,前面用0补充
foo.count(); //返回1的个数
foo.size(); //返回位数
2、取余,%
利用 % 来判断最后一位是不是2,也就是二进制中的1。
3、位运算,&1
每次 &1,如果最后一位是1,则计数+1,n 右移1位。
4、位运算,n & (n - 1)
把一个整数减去1,再和原整数做与运算,会把该整数最右边一个1变成0,那么一个整数的二进制有多少个1,就可以进行多少次这样的操作。
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
return bitset<32>(n).count();
}
};class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int cnt = 0;
while(n != 0){
cnt += n % 2;
n /= 2;
}
return cnt;
}
};class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int cnt = 0;
while(n != 0){
if(n&1 != 0){
++cnt;
}
n >>= 1;
}
return cnt;
}
};class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int cnt = 0;
while(n != 0){
n = n & (n - 1);
++cnt;
}
return cnt;
}
};剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方
快速幂算法
1、分治法
2、倍增法(基于位运算):标准的快速幂算法
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, long long n) {
return n > 0? myPowHelper(x, n): 1.0 / myPowHelper(x, -n);
}
double myPowHelper(double x, long long n){
if(n == 0) return 1;
if(n == 1) return x;
double tmp = myPowHelper(x, n/2);
if(n%2 == 0){
return tmp * tmp;
}else{
return tmp * tmp * x;
}
}
};class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, long long n) {
return n > 0? fastPow(x, n): 1.0 / fastPow(x, -n);
}
double fastPow(double x, long long n){
double ans = 1.0;
while(n){
if(n & 1)
ans *= x;
x *= x;
n >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
};剑指 Offer 17. 打印从1到最大的n位数
最大 n 位数
最大的 n 位数(记为 end )和位数 n 的关系:
如果 n 的数据很大的情况下,end 会溢出,无法正常存储,需要考虑大数越界问题。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printNumbers(int n) {
vector<int> ans;
int end = pow(10, n) - 1;
for(int i=1; i<=end; ++i){
ans.push_back(i);
}
return ans;
}
};剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
链表删除节点
1、单指针:找到要删除节点的前一个节点,注意头节点就是要删除的节点的情况。
2、双指针:找到要删除节点和要删除节点的前一个节点和,注意头节点就是要删除的节点的情况。
3、单指针/双指针 + 虚拟头节点:这样就不用考虑头节点就是要删除的节点的情况了。
4、递归:找到删除的节点时返回该节点的下一个,否则返回当前节点。
5、栈或数组等数据结构:遍历链表,将值不等于 val 的节点依次压入栈中;再将链表的节点重新连接。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
if(head->val == val){
return head->next;
}
ListNode *pre = head;
while((pre->next != NULL) && (pre->next->val != val)){
pre = pre->next;
}
if(pre->next != NULL){
pre->next = pre->next->next;
}
return head;
}
};class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
if(head->val == val){
return head->next;
}
ListNode *pre = head;
ListNode *cur = head;
while((cur != NULL) && (cur->val != val)){
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
if(cur != NULL){
pre->next = cur->next;
}
return head;
}
};class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode *pre = dummy;
while((pre->next != NULL) && (pre->next->val != val)){
pre = pre->next;
}
if(pre->next != NULL){
pre->next = pre->next->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
if(head == NULL){
return head;
}
head->next = deleteNode(head->next, val);
return head->val == val? head->next: head;
}
};剑指 Offer 19. 正则表达式匹配
字符串编辑
动态规划
二维数组 dp[i][j] 表示:s[0] ~ s[i - 1] 和 p[0] ~ p [j - 1]是否匹配。根据字符、星号,点号,分情况讨论来更新 dp 数组。
class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
int m = s.size(), n = p.size();
vector<vector<bool>> dp(m + 1, vector<bool>(n + 1, false));
// 初始化 空串情况
dp[0][0] = true;
// 初始化第一行,如果有*,考虑匹配结果
for(int j=1; j<n+1; ++j){
// 按题意p第一个字符不可能为*,所以不会越界
if(p[j-1] == '*'){
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-2];
}
}
for(int i=1; i<m+1; ++i){
for(int j=1; j<n+1; ++j){
if(s[i-1] == p[j-1] || p[j-1] == '.'){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1];
}else if(s[i-1] != p[j-1] && p[j-1] != '*' && p[j-1] != '.'){
dp[i][j] = false;
}else if(p[j-1] == '*'){
if(s[i-1] == p[j-2] || p[j-2] == '.'){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] || dp[i][j-2];
} else{
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-2];
}
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};剑指 Offer 20. 表示数值的字符串
字符串编辑
1、模拟:根据题目要求,模拟字符串是数值的条件
2、确定有限状态自动机(DFA)
3、正则表达式
class Solution {
public:
bool isNumber(string s) {
if(s.size() == 0){
return false;
}
int index = 0;
// 空格遍历下一个
while(s[index] == ' '){
++index;
}
bool numeric = scanInteger(s, index);
// 判断小数部分:.123 或 123. 或 123.456
if(s[index] == '.'){
++index;
numeric = scanUnsignedInteger(s, index) || numeric;
// 注意不能是 numeric = numeric || scanUnsignedInteger(s, index);
// 因为如果 numeric == true,就不会扫描.后面的部分,也就不会改变index的值了
}
// 判断指数部分:1e5 或 1e+5
if(s[index] == 'e' || s[index] == 'E'){
++index;
numeric = scanInteger(s, index) && numeric;
}
// 空格遍历下一个
while(s[index] == ' '){
++index;
}
return numeric && index == s.size();
}
// 判断是否是整数:[+|-]A
bool scanInteger(const string s, int& index){
if(s[index] == '+' || s[index] == '-'){
++index;
}
return scanUnsignedInteger(s, index);
}
// 判断是否是无符号整数:A
bool scanUnsignedInteger(const string s, int& index){
int temp = index;
while(index != s.size() && s[index] >= '0' && s[index] <= '9'){
++index;
}
return index > temp;
}
};剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
数组元素修改
1、单指针 + 两次遍历
2、首尾双指针 + 一次遍历
3、原地交换 + 一次遍历
定义 i,j 首尾双指针,i 从左侧往右开始遍历,如果遇到的是奇数,就表示这个元素已经调整完成了,继续从左往右遍历,直到遇到一个偶数。j 从右侧往左开始遍历,如果遇到的是偶数,就表示这个元素已经调整完成了,继续从右往左遍历,直到遇到一个奇数。交换这个偶数和奇数的位置,并且重复两边的遍历,直到在中间相遇。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> ans;
for(auto num: nums){
if(num % 2 != 0){
ans.push_back(num);
}
}
for(auto num: nums){
if(num % 2 == 0){
ans.push_back(num);
}
}
return ans;
}
};class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> ans(n, 0);
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
for(auto num: nums){
if(num % 2 != 0){
ans[i++] = num;
}else{
ans[j--] = num;
}
}
return ans;
}
};class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
while(i < j){
while(i < j && nums[i]%2 == 1){
++i;
}
while(i < j && nums[j]%2 == 0){
--j;
}
if(i < j){
swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
}
}
return nums;
}
};剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
链表遍历
1、遍历,记录链表元素个数
2、快慢指针,快指针先走 k 步,再和慢指针一起走,一起走时,两个指针共走了全部的元素。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
int cnt = 0;
ListNode *node = head;
while(node != NULL){
++cnt;
node = node->next;
}
cnt = cnt - k;
while(cnt--){
head = head->next;
}
return head;
}
};class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode *fast = head;
ListNode *slow = head;
while(fast != NULL && k > 0){
fast = fast->next;
--k;
}
while(fast != NULL){
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
};剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
链表反转
1、三个变量迭代(头插法):链表指针转向,变量指针移动
2、递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *prev = NULL, *next = NULL;
while(head != NULL){
next = head->next;
head->next = prev;
prev = head;
head = next;
}
return prev;
}
};class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head, ListNode* prev = nullptr) {
if(!head){
return prev;
}
ListNode* next = head->next;
head->next = prev;
return reverseList(next, head);
}
};剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
合并链表
遍历两个链表,元素比较,将小的元素添加到新的链表中,直到其中一个链表遍历到末尾,将另一个链表的剩余部分添加到新链表中。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* node = dummy;
while(l1 && l2){
if(l1->val > l2->val){
node->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}else{
node->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
node = node->next;
}
node->next = l1? l1: l2;
return dummy->next;
}
};剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
树的子结构
递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubStructure(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
if(A == NULL || B == NULL){
return false;
}
// 当前节点开始比较 或 左子树 或 右子树
return isSubStructureHelper(A, B) || isSubStructure(A->left, B) || isSubStructure(A->right, B);
}
bool isSubStructureHelper(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
if(B == NULL) return true;
if(A == NULL) return false;
// 当前节点相同继续比较左子树和右子树
if(A->val == B->val){
return isSubStructureHelper(A->left, B->left) && isSubStructureHelper(A->right, B->right);
}else{
return false;
}
}
};剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像
翻转二叉树
1、递归:交换左右子树的元素
2、借助队列或者栈:类似于层序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return NULL;
}
swap(root->left, root->right);
mirrorTree(root->left);
mirrorTree(root->right);
return root;
}
};class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return NULL;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
if(node){
q.push(node->left);
q.push(node->right);
swap(node->left, node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return NULL;
}
stack<TreeNode*> s;
s.push(root);
while(!s.empty()){
TreeNode* node = s.top();
s.pop();
if(node){
s.push(node->left);
s.push(node->right);
swap(node->left, node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树
对称二叉树
1、递归:左的右 == 右的左
2、借助队列或者栈:类似于层序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return true;
}
return isSymmetricHelper(root->left, root->right);
}
bool isSymmetricHelper(TreeNode* l, TreeNode* r) {
if(l == NULL && r == NULL){
return true;
}
if(l == NULL || r == NULL || l->val != r->val){
return false;
}
return isSymmetricHelper(l->left, r->right) && isSymmetricHelper(l->right, r->left);
}
};class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return true;
}
return isSymmetricHelper(root->left, root->right);
}
bool isSymmetricHelper(TreeNode* l, TreeNode* r) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(l); q.push(r);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* node1 = q.front(); q.pop();
TreeNode* node2 = q.front(); q.pop();
if(node1 == NULL && node2 == NULL){
continue;
}
if(node1 == NULL || node2 == NULL){
return false;
}
if(node1->val != node2->val){
return false;
}
q.push(node1->left); q.push(node2->right);
q.push(node1->right); q.push(node2->left);
}
return true;
}
};剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
矩阵遍历
模拟:根据题意,定义四个指针变量,不断移动移动,将矩阵元素顺时针添加到新数组中。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
if(matrix.size() == 0){
return vector<int>();
}
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> ans;
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
int top = 0, bottom = m - 1;
while(left <= right && top <= bottom){
// 向右
for(int j=left; j<=right; ++j){
ans.push_back(matrix[top][j]);
}
if(++top > bottom) break;
// 向下
for(int i=top; i<=bottom; ++i){
ans.push_back(matrix[i][right]);
}
// 向左
if(--right < left) break;
for(int j=right; j>=left; --j){
ans.push_back(matrix[bottom][j]);
}
// 向上
if(--bottom < top) break;
for(int i=bottom; i>=top; --i){
ans.push_back(matrix[i][left]);
}
if(++left > right) break;
}
return ans;
}
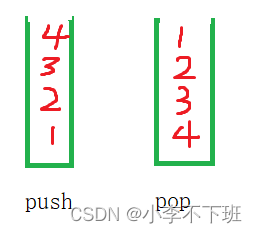
};剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
最小栈
1、辅助栈:栈顶表示当前原栈里所有值的最小值
2、不使用额外栈:每次添加元素时,压入最小值和压入新元素,栈顶下一个元素表示最小值。
class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
stack<int> s, min_s;
MinStack() {
//min_s.push(INT_MAX);
}
void push(int x) {
s.push(x);
if(min_s.empty() || min_s.top() >= x){
min_s.push(x);
}
}
void pop() {
if(!min_s.empty() && min_s.top() == s.top()){
min_s.pop();
}
s.pop();
}
int top() {
return s.top();
}
int min() {
return min_s.top();
}
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();
* obj->push(x);
* obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* int param_4 = obj->min();
*/class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
stack<int> s;
int minNum = INT_MAX;
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
minNum = std::min(minNum, x);
s.push(minNum);
s.push(x);
}
void pop() {
s.pop();
s.pop();
if(!s.empty()){
int tmp = s.top();
s.pop();
minNum = s.top();
s.push(tmp);
}else{ // 注意要恢复初始值
minNum = INT_MAX;
}
}
int top() {
return s.top();
}
int min() {
return minNum;
}
};剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
验证栈序列
辅助栈:将压入序列中的元素压入新栈中,当元素和弹出序列中的元素相同时开始出栈,index++,最终栈为空则证明栈序列正确。
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
if(pushed.size() != popped.size()){
return false;
}
if(pushed.size() == 0 && popped.size() == 0){
return true;
}
int len = pushed.size();
stack<int> s;
int popIndex = 0;
for(int i=0; i<len; ++i){
s.push(pushed[i]);
while(!s.empty() && popIndex < len && s.top() == popped[popIndex]){
++popIndex;
s.pop();
}
}
return s.empty();
}
};剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
层序遍历
最基础的层序遍历,借助队列即可。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return vector<int>();
}
vector<int> ans;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
root = q.front();
q.pop();
ans.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left){
q.push(root->left);
}
if(root->right){
q.push(root->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
层序遍历——按层打印
与 I 相比,II 要求按层打印,也就是将每一层的元素分别保存到一维数组中。
方法1:利用队列的.size(),来确定每一层元素的个数。
ret.push_back(vector <int> ()); 在结果数组(ret, 二维)中添加一个新的数组(一维,空)用于保存每一层的节点。
ret.back().push_back(node->val); 获取结果数组(ret, 二维)中最后一个数组(一维,保存当前层节点的数组),并在该数组中添加节点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return vector<vector<int>>();
}
vector<vector<int>> ans;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int cnt = q.size();
ans.push_back(vector<int>());
for(int i=0; i<cnt; ++i){
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
ans.back().push_back(node->val);
if(node->left){
q.push(node->left);
}
if(node->right){
q.push(node->right);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III
层序遍历——Z型打印
与 II 相比,III 要求按照 Z型/锯齿型 打印,在选择每一层从左向右还是从右向左时,定义一个变量 isOrderLeft 来保证隔行打印方向是一样的,使用双端队列 deque 更加方便的添加元素,最终再加入到 ans 结果数组中。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return vector<vector<int>>();
}
vector<vector<int>> ans;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
bool isOrderLeft = true;
while(!q.empty()){
int cnt = q.size();
deque<int> levelList;
for(int i=0; i<cnt; ++i){
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
if(isOrderLeft){
levelList.push_back(node->val);
}else{
levelList.push_front(node->val);
}
if(node->left){
q.push(node->left);
}
if(node->right){
q.push(node->right);
}
}
ans.emplace_back(levelList.begin(), levelList.end());
isOrderLeft = !isOrderLeft;
}
return ans;
}
};剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
验证后序遍历
递归
后序遍历最后一个元素就是根,由于是题目是二叉搜索树,找到第一个大于根的元素,这个元素前面是左子树,均小于根,后面是右子树,均大于根。判断是否符合上述要求,如果符合递归的验证左右子树部分。
class Solution {
public:
bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& postorder) {
if(postorder.empty() || postorder.size() == 1){
return true;
}
return verifyPostorderHelper(postorder, 0, postorder.size()-1);
}
bool verifyPostorderHelper(vector<int>& postorder, int low, int high) {
if(low >= high){
return true;
}
int start = low;
while(start < high && postorder[start] < postorder[high]){
++start;
}
for(int i=start; i<high; ++i){
if(postorder[i] <= postorder[high]){
return false;
}
}
return verifyPostorderHelper(postorder, low, start-1) && verifyPostorderHelper(postorder, start, high-1);
}
};剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
路径总和
递归、回溯
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int target) {
pathSumHelper(root, target);
return res;
}
void pathSumHelper(TreeNode* root, int tar) {
if(root == nullptr){
return;
}
path.push_back(root->val);
tar -= root->val;
if(tar == 0 && root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr){
res.push_back(path);
}
pathSumHelper(root->left, tar);
pathSumHelper(root->right, tar);
path.pop_back(); // 回溯:说明当前节点不满足要求,pop掉,返回其父亲节点
}
};剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
复制带随机指针的链表
深拷贝
1、哈希表 + 回溯 O(n)、O(n)
哈希表记录每一个节点对应新节点的创建情况。遍历该链表的过程中,检查「当前节点的后继节点」和「当前节点的随机指针指向的节点」的创建情况。
如果这两个节点中的任何一个节点的新节点没有被创建,我们都立刻递归地进行创建。当我们拷贝完成,回溯到当前层时,我们即可完成当前节点的指针赋值。注意一个节点可能被多个其他节点指向,因此我们可能递归地多次尝试拷贝某个节点,为了防止重复拷贝,我们需要首先检查当前节点是否被拷贝过,如果已经拷贝过,我们可以直接从哈希表中取出拷贝后的节点的指针并返回即可。
2、迭代:新节点插入再拆分 O(n)、O(1)
把复制的节点插到原结点后面,复杂指针的指向去原结点找,复制节点的随机指针指向原节点的随机指针的下一个。
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> cachedNode;
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == NULL){
return NULL;
}
if(!cachedNode.count(head)){ // 当前节点未拷贝
Node* newNode = new Node(head->val);
cachedNode[head] = newNode;
newNode->next = copyRandomList(head->next);
newNode->random = copyRandomList(head->random);
}
return cachedNode[head];
}
};class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == NULL){
return NULL;
}
// 将拷贝节点放到原节点后面,例如1->2->3变成了1->1'->2->2'->3->3'
for(Node* node = head; node != NULL; node = node->next->next){
Node* newNode = new Node(node->val);
newNode->next = node->next;
node->next = newNode;
}
// 处理拷贝节点的random指针
for(Node* node = head; node != NULL; node = node->next->next){
Node* newNode = node->next;
if(node->random == NULL){
newNode->random = NULL;
}else{
// 注意是指向拷贝节点,不是源节点的node->random,否则拆分时会出现问题
newNode->random = node->random->next;
}
}
// 拆分拷贝节点和原节点,变成1->2->3和1'->2'->3'两个链表
Node* newHead = head->next;
for(Node* node = head; node != NULL; node = node->next){
Node* newNode = node->next;
node->next = node->next->next;
if(newNode->next == NULL){
newNode->next = NULL;
}else{
newNode->next = newNode->next->next;
}
}
return newHead;
}
};
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
二叉搜索树与双向链表
中序遍历、递归
中序遍历的结果就是链表元素的顺序,设置头节点、前驱节点和当前节点,连接节点。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node *head = NULL;
Node *pre = NULL;
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == NULL) return NULL;
dfs(root);
// 首位连接
head->left = pre;
pre->right = head;
return head;
}
void dfs(Node* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return;
// 左 根 右
dfs(cur->left);
if(pre == NULL){ // 当前节点是第一个节点
head = cur;
pre = cur;
}else{
cur->left = pre;
pre->right = cur;
pre = cur;
}
dfs(cur->right);
}
};剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树
二叉树序列化与反序列化
加密与解密
1、bfs,层序遍历
2、dfs,前序遍历
可以使用 istringstream(string str) 来读取字符。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return "";
}
string data;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
// null用#表示,元素间用空格分隔
if (node) {
data += to_string(node->val) + ' ';
q.push(node->left);
q.push(node->right);
} else {
data += "# ";
}
}
// 删除最后一个空格
if (!data.empty()){
data.pop_back();
}
return data;
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
if(data.empty()){
return NULL;
}
vector<TreeNode*> nodes; // 保存节点
for(int i=0; i<data.size(); ++i){
if(data[i] == ' ') continue;
if(data[i] == '#'){
nodes.push_back(NULL);
continue;
}
// 找到以空格分隔的子串转换为int元素
int begin = i, end = i;
while(data[end] != ' '){
++end;
}
string sub = data.substr(begin, end-begin);
nodes.push_back(new TreeNode(atoi(sub.c_str())));
i = end;
}
// 将节点连接,返回头节点即可
int pos = 1;
for(int i=0; i<nodes.size(); ++i){
if(nodes[i] == NULL){
continue;
}else{
nodes[i]->left = nodes[pos++];
nodes[i]->right = nodes[pos++];
}
}
return nodes[0];
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec;
// codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return "#";
}
return to_string(root->val) + " " + serialize(root->left) + " " + serialize(root->right);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
istringstream temp(data);
return des(temp);
}
TreeNode *des(istringstream& ss){
string sub;
ss >> sub;
if(sub == "#"){
return NULL;
}
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(stoi(sub));
node->left = des(ss);
node->right = des(ss);
return node;
}
};剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
全排列
1、
next_permutation()
C++的STL提供求「下一个」排列组合的函数next_permutation()
- 函数
next_permutation()的定义有两种形式:
bool next_permutation (BidirectionalIterator first, BidirectionalIterator last);bool next_permutation (BidirectionalIterator first, BidirectionalIterator last, Compare comp);- 返回值
:如果没有下一个排列组合,返回false,否则返回true。每执行next_permutation()一次,会把新的排列放到原来的空间里。- 注意
:它排列的范围是 [first,last),包括first,不包括last。- 补充
:next_permutation()是从当前的全排列开始,逐个输出更大的全排列,而不是输出所有的全排列。如果要得到所有的全排列,先使用sort排序,得到最小排列后,然后再使用next_permutation()就可以了。2、自写全排列函数:dfs + 回溯 + 去重
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
vector<string> res;
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
do{
res.push_back(s);
}while(next_permutation(s.begin(), s.end()));
return res;
}
};class Solution {
public:
vector<string> res;
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
dfs(s, 0, s.size()-1);
return res;
}
set<string> st; // set去重
void dfs(string& str, int s, int t){ // 从第s个数开始到第t个结束的全排列
if(s == t){ // 递归结束,产生一个全排列
if(st.find(str) == st.end()){
st.insert(str);
res.push_back(str);
}
return;
}
for(int i=s; i<=t; ++i){
swap(str[s], str[i]); // 把当前第1个数与后面所有数交换位置
dfs(str, s+1, t);
swap(str[s], str[i]); // 恢复,用于下一次交换
}
}
};class Solution {
public:
vector<string> res;
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
if(s.size() == 0){
return vector<string>();
}
dfs(s, 0, s.size()-1);
sort(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
void dfs(string& str, int s, int t){
if(s == t){
res.push_back(str);
return;
}
unordered_map<int, bool> vis;
// set<int> st;
for(int i=s; i<=t; ++i){
if(vis[str[i]] == true){
continue;
}
// if(st.find(str[i]) != st.end()){
// continue;
// }
vis[str[i]] = true;
// st.insert(str[i]);
swap(str[s], str[i]);
dfs(str, s+1, t);
swap(str[s], str[i]);
}
}
};剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
多数元素
1、排序 O(nlogn)、O(logn)
如果将数组
nums中的所有元素按照单调的顺序排序,那么下标为 n/2 的元素(下标从 0 开始)一定是众数。2、哈希表 O(n)、O(n)
遍历数组
nums,用 HashMap 统计各数字的数量,即可找出 众数 。3、摩尔投票法(Boyer-Moore) O(n)、O(1)
摩尔投票法,核心理念为 票数正负抵消,成立前提就是有出现超过一半的元素。
设输入数组
nums的众数为 x ,数组长度为 n 。推论一: 若记 众数 的票数为 +1 ,非众数 的票数为 -1 ,则一定有所有数字的票数和 > 0 。
推论二: 若数组的前 a 个数字的 票数和 = 0,则 数组剩余 (n-a) 个数字的票数和一定仍 >0 ,即后 (n-a) 个数字的 众数 仍为 x 。
根据以上推论,记数组首个元素为 n1,众数为 x ,遍历并统计票数。当发生 票数和 = 0 时,剩余数组的众数一定不变 ,这是由于:
当 n1 = x :抵消的所有数字中,有一半是众数 x 。
当 n1 != x:抵消的所有数字中,众数 x 的数量最少为 0 个,最多为一半。
利用此特性,每轮假设发生 票数和 = 0 都可以缩小剩余数组区间 。当遍历完成时,最后一轮假设的数字即为众数。
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
return nums[nums.size() / 2];
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> hash;
for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); ++i){
hash[nums[i]]++;
if(hash[nums[i]] > nums.size()/2){
return nums[i];
}
}
return 0;
}
};class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
int votes = 0, x = 0;
for(int num: nums){
if(votes == 0){
x = num;
}
votes += num == x? 1: -1;
}
// 验证x是否为众数
int cnt = 0;
for(int num: nums){
if(num == x){
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt > nums.size()/2? x: 0;
}
};觉得文章还不错,可以点个小赞赞,支持一下哈!